
HyperScope® − 100% in-line hyperspectral seal inspection for trays, pots and thermoforms

HyperScope® is a new in-line, 100% seal inspection system using hyperspectral imaging that detects foreign materials or contamination in the sealing area of rigid packages, such as trays, pots and containers. The inspection system features GPU-accelerated artificial intelligence, which enables high-precision seal area detection in real-time, regardless of the package orientation, packaging material, layout or size. Another new improvement is the (optionally) integrated conveyor belt that can be completed with an integrated reject unit. Hyperspectral camera technology enables to identify substances with different compositions such as plastics, paper, organic product, fat, liquids with a much higher contrast than traditional vision-based camera systems. In addition, when printed film is used, hyperspectral is the only imaging technology that detects contamination through the plastic top film reliably.
DOWNLOAD BROCHURE HYPERSCOPE REQUEST INFO OR DEMO WATCH WEBINAR
HYPERSCOPE: HOW IT WORKS
HyperScope® generates an image with a much higher contrast revealing more information than a standard vision camera. The camera can detect contamination through plastic foils – even when printed.
In detail:
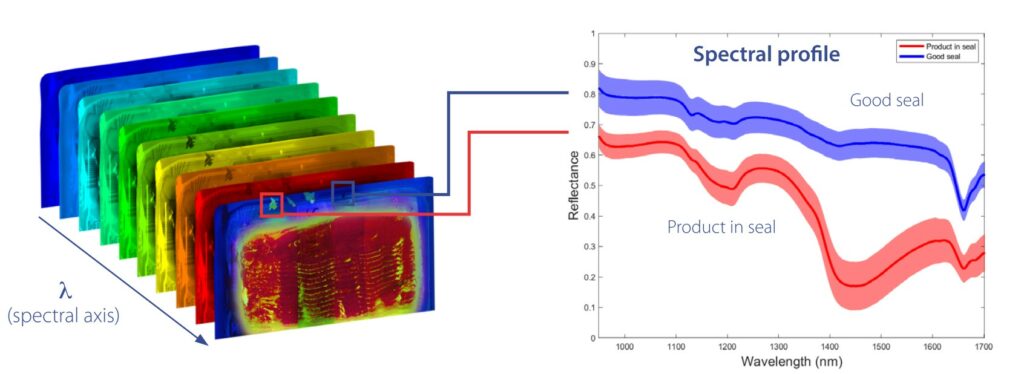
- HyperScope® measures a spectral profile over a broad wavelength range
- Depending on the camera type this ranges from visual (400 nm) over near-infrared (950nm) to short wave infrared light (1700nm)
- Near-infrared light with longer wavelengths is transmitted and reflected through the sealing film, even when printed
- The spectral profile of the package is built from the reflecting light containing information on the materials in the package and sealing area
- Substances such as plastics, organic product, fat, liquids have a unique spectral profile and can be identified in different wavelength bands
 |
 |
| A standard industrial camera image is built from 3 wavelengths ranges (RGB) and only provides visible information. | The hyperspectral 3D spectral image map is built from a broad wavelength spectrum. Every pixel is analyzed individually and differences in materials or composition are detected, even through printed foil. A contaminated seal has a different spectral profile than a clean seal. |
IN-LINE SEAL INSPECTION SETUP
Every individual package is inspected at 160 ppm and results are analyzed in real-time. Immediate feedback on the sealing quality is displayed on the controller touch screen. A reject signal is sent to an ejector to eliminate defective packages.


BENEFITS & FEATURES
| Benefits | Features |
|
|
SEAL INSPECTION EXAMPLES
Importance of detecting seal contamination
Seal contamination in food packages leads to leakage, growth of molds or bacteria and consequently reduced shelf-life, health risks and even expensive recalls. Automatic detection of contaminated seals that can lead to leaks is essential for both food safety and production automation.

Example: Sliced cheese (plastic tray with printed foil)
This example demonstrates seal inspection on trays with sliced cheese. Some of the packages have a contamination such as a small parts of cheese in the seal. Because the film is printed, the contamination is not visible to the human eye or to a vision camera.
| Visual image When product and film have similar colors (e.g. yellow-on-yellow), contamination in the seal is not or hardly visible |
 |
Hyperspectral image result The higher contrast reveals contamination (red) in the sealing area (green mask) |
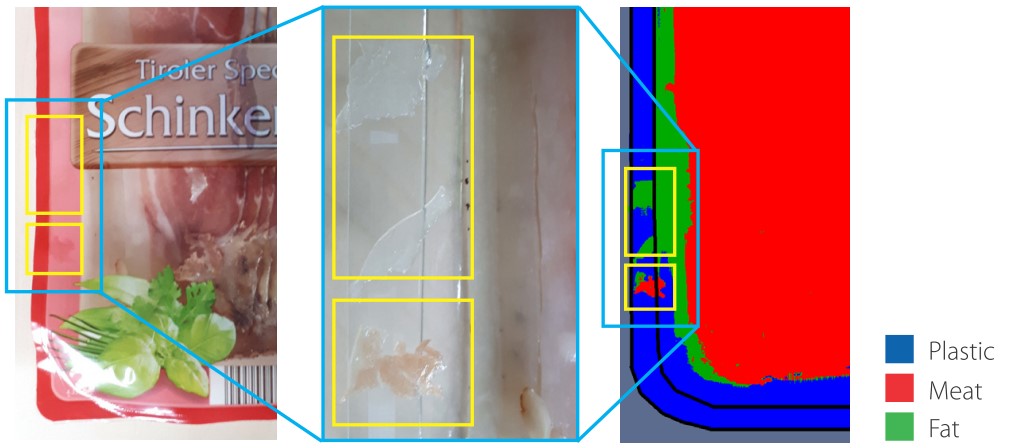
Example: Sliced ham (plastic tray with printed foil)
This is an example where fat and meat are present in the seal. Due to the printed top film, both materials are not visible. With the higher contrast, hyperspectral imaging allows to detect and classify both substances.
APPLICATIONS
Seal inspection
Contamination detection in seals of trays, pots and other thermo-formed packages:
| • Cheese • Fillets • Sliced meat • Minced meat |
• Ready meals • Fresh produce • Snacks • etc. |
 |
|
Other food inspection applications
Incoming goods inspection for food or pet care:
• Content composition (e.g. meat, fat, liquids)
• Detection of foreign bodies
• Checking presence of correct content (in case of printed foil)
